Resistivity of Various Materials
Resistivity of Various Materials: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Materials, Classification of Materials, Insulators, Semiconductors, Resistivity of Various Materials, Types of Resistors, Wire Bound Resistors and Carbon Resistors.
Important Questions on Resistivity of Various Materials
Resistance of a carbon resistor determined from colour codes is () . The colour of the third band must be :
Wire bound resistors are made by
The resistance of mercury _____ as the temperature increases.
Resistivity is the characteristic property of the material of the conductor and does not depend on the length and cross-sectional area of the conductor. Most appropriate reason that is:
When light shines on a junction diode, the current versus voltage is observed as in figure below.
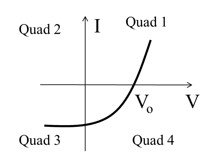
In which quadrant(s) does the diode generate power, so that it can be used as a solar cell?
The -side of the depletion layer of a junction
The carbon resistor can produce a high accuracy value of ___________.
Which of the following materials is an insulator?
A solar cell is to be fabricated for efficient conversion of solar radiation to emf using material The solar cell is to be mechanically protected with the help of a coating using material If the band gap energy of materials and are and respectively, then which of the following choices is optimum for better performance of the solar cell.
If copper and silicon pieces are heated, the resistance of
Which raw material is predominantly used in household industries?
Which of the following materials was commonly used by the Harappans for the construction of their buildings?
Which of the following was a common material used for making tools in the Harappan Civilization?
Which metal was commonly used by the Harappans for making tools and ornaments?
What was the main strategy of the Non-Cooperation Movement?
Which British law did the Non-Cooperation Movement aim to oppose?
Which group was primarily involved in the revolt in Awadh?
If a copper wire is stretched to make its radius decrease by , then the percentage increase in resistance is nearly
Assertion: The resistivity of the semiconductor decreases with increase of temperature.
Reason: In a conducting solid, the rate of collision between free electrons and ions increases with increase of temperature.
A solid which is transparent to visible light and whose conductivity increases with temperature is formed by
